SuperTurbo with Turbine Bypass for Cold Start Aftertreatment Heating
Upcoming regulations such as California’s Low NOx Omnibus and Euro VII will require >90% reductions in tailpipe NOx emissions from heavy-duty trucks. This is a series providing a summary of various technologies which can help meet these challenging regulations.

What is a SuperTurbo?
SuperTurbo is a driven turbocharger that has the capability of mechanically transferring power to and from the turbo shaft, enabling both compounding of excess turbine energy, as well as supercharging capability for improved transient response and greater control over charge flow. This supercharging capability also allows for a complete turbine bypass to be used during engine cold start, while still providing boosted airflow to the engine. For heavy duty diesel engines, this ability to supercharge during times of zero flow to the turbine is important to retain drivability and functionality of the engine. The turbine bypass directs the hot exhaust gasses directly to the aftertreatment, resulting in rapid heating of the aftertreatment during a cold start.
See the end of this article for a short video which explains the bypass operation.
Benefits for lower NOx emissions
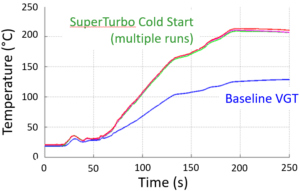
Preliminary testing of the SuperTurbo with the turbine bypass has shown very promising results for enabling NOx reduction early on during an engine cold start. Testing at Southwest Research Institute (SWRI) for the CARB Stage 3 Low NOx program showed that this system provided the most rapid heating of the aftertreatment of any of the technologies tested by a wide margin on the cold FTP cycle.
Follow up testing on the cold WHTC cycle also shows much improved aftertreatment warm up compared to the base engine, with a corresponding improvement in NOx conversion early in the cycle, even with the stock aftertreatment and ECU calibration.
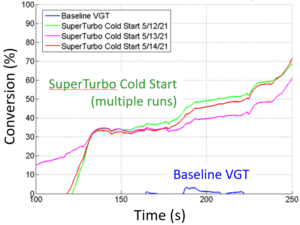
What about fuel consumption ?
During times when the turbine bypass is active, the supercharging capability does result in increased fuel consumption of the engine. However, since the aftertreatment is rapidly heated, the engine can revert to more typical, efficient operation earlier in the cold start cycle, and even employ engine stop-start early in the cycle to save fuel. During testing at SWRI aggressive fueling during the first long idle period of the cold FTP was utilized to help heat the aftertreatment; it was noted that when using the SuperTurbo with the turbine bypass that this idle period had a cooling effect on the aftertreatment instead, as the aftertreatment temperatures when using the SuperTurbo were much greater than the other technologies. Follow-up testing employed engine stop-start during this first long idle, as well as the second long idle, which resulted in substantial fuel savings. Using stop-start early in the cold FTP cycle indicated a potential to reduce fuel consumption to baseline levels or even below, while still rapidly heating the aftertreatment and drastically improving early cold cycle NOx conversion.
Here is a short video on bypass operation for early catalyst warm-up:
For more information visit SuperTurbo Technologies
Like it ? Share it !
