U.S. EPA proposes to revise annual PM2.5 standard from 12 ug/m3 to 9 - 10 ug/m3
Link to EPA announcement and proposal document
Ultrafine particles, defined as those less than 2.5 microns in diameter and denoted as PM2.5, have long been associated with adverse health effects. These particles penetrate deep into the lungs, known to migrate to various organs including the brain, and even associated with affecting learning abilities in school children. The references are too many to list here, but the EPA’s integrated science assessment for particulate matter is one place to start reading. Moreover, a growing pool of studies on environmental justice shows that – as is often the case – the poor and minorities suffer more than their fair share of the health burden of air pollution.
Taking into account the latest evidence and the need to continue driving down air pollutants, the US EPA has proposed to revise the annual PM2.5 national ambient air quality standard (NAAQS) from 12 ug/m3 (micrograms per cubic meter) to a level of 9 – 10 ug/m3.
If that change doesn’t sound like a lot, you are both right and wrong.
Right in that we have come a long way since the hazy smog days of Los Angeles in the 1970s and that most of the US enjoys significantly clean air compared to some of the busiest cities such as Beijing and New Delhi which record 3-digit concentrations.
Wrong in that each microgram of reduction is absolutely essential – and associated with improved health outcomes. A major study covering 61 million individuals concluded that “a 10-μg/m3 increase in PM2.5 was found to be associated with a 7.3% (95% CI, 7.1%–7.5%) increase in mortality for a given ZIP code”.
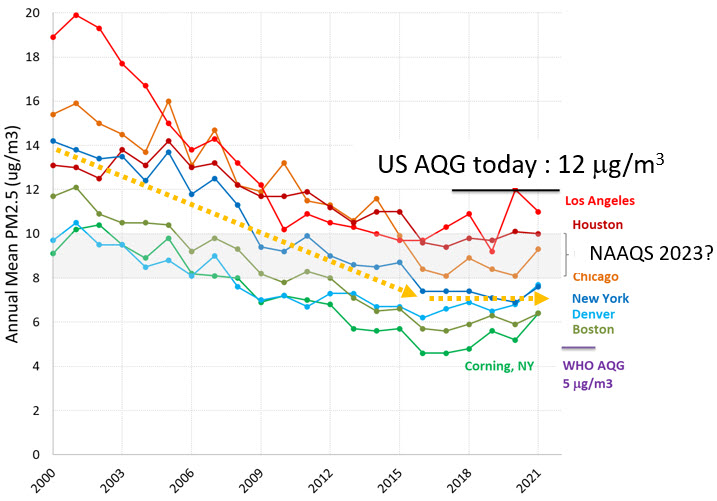
This figure on the right shows some recent data collected by the EPA which shows that averaged over the year, several cities have PM2.5 concentrations below the current annual air quality guidelines. Great progress done over these last two decades, but we are beginning to plateau. And note that the levels are still above the recently announced guidelines by the World Health Organization of 5 ug/m3 for good health.
So what does it mean and what next ?
There is a 60-day comment period, and the EPA will issue the final rule later in the year.
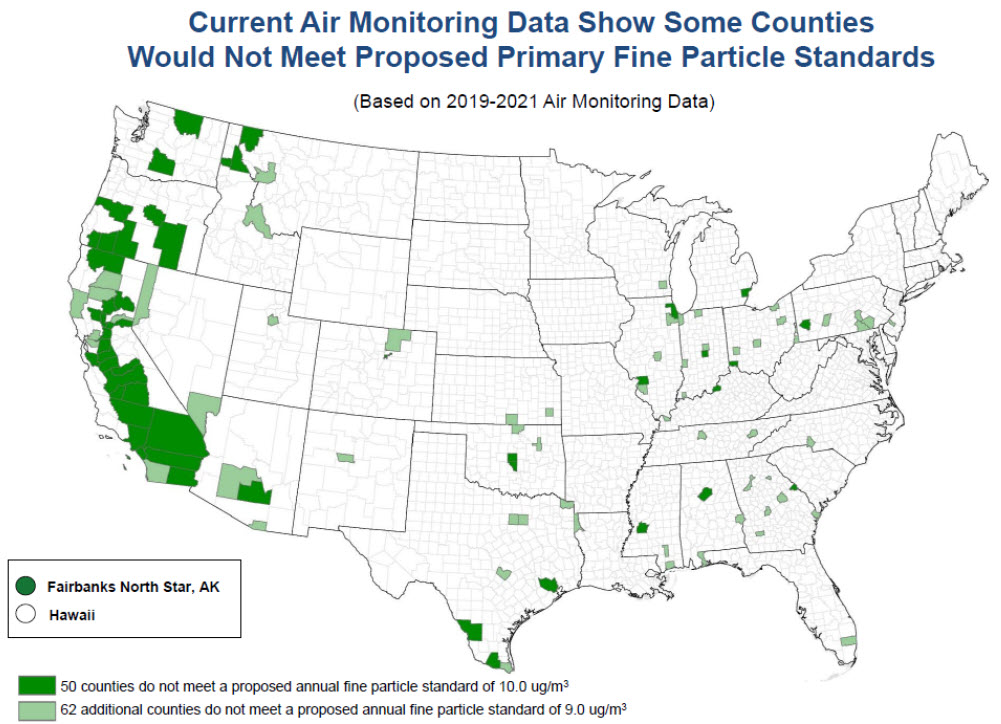
The revised NAAQS will result in several areas in the country to be out of attainment – see figure on the right taken from the EPA summary presentation (link in the title of this article).
The Clean Air Act requires EPA and states to take steps for ensuring that all areas meet the revised standards.
Within two years after the final NAAQS rule, EPA has to designate areas to be either in attainment or not, based on 3 years of air quality monitoring data.
States then have to submit state implementation plans (or SIPs) which outline how the state intends to meet the revised NAAQS no later than 6 years after the designations.
Ultimately, new emissions standards on vehicular and stationary sources will be required to help these areas get back in attainment. (In case you were wondering how transportation fits in all of this ..)
If you like such content, check out the monthly newsletter covering the latest on sustainable transportation technologies and regulations. Sign up below.
Like it ? Share it !
Other recent posts
China Stage 4 Fuel Consumption Standard for Light Commercial Vehicles
A summary of Chinese Stage 4 fuel consumption standards for light commercial vehicles.
Mobility in India – excerpts of recent headlines
A summary of reports from a couple of leading newspapers in India, taken during end of Sept to early October, 2024 points to the rapidly changing mobility and energy landscape in India.
Biofuels summit in Washington DC highlights role of ethanol in transport decarbonization
The biofuels summit hosted by Growth Energy at Washington DC highlighted the role that ethanol continues to play in decarbonizing the transport sector.
