Daimler's new 15L heavy-duty engine : Primed to meet upcoming low NOx and GHG regulations
Daimler Truck AG described the features of their new Detroit DD15 engine at the 42nd International Vienna Motor Symposium. This is a summary of that paper / presentation.
Background
Daimler Truck has improved it’s 15L engine for Class 8 long-haul trucks in North America. The model year 2021 Detroit DD15 engine has to comply with the first step of the greenhouse gas (GHG) phase 2 regulations in the US – the other steps are in 2024 and 2027 – while also demonstrating NOx compliance over 435,000 miles. And future HD regulations in California will require further reductions in NOx, so this engine is a good step along the way to future improvements. This article covers a few of the discussed improvements.
Summary
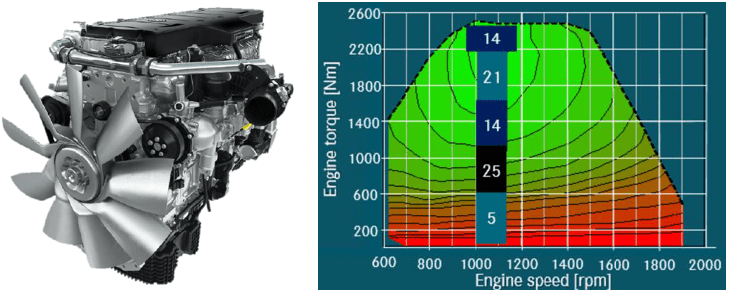
This is a 15L 6-cylinder inline engine, delivering > 48% BTE over a wide region of the engine map. The combination of engine measures, control systems and after-treatment enables it to already meet the 2024 GHG standards, while significantly reducing NOx emissions.
Key Enabling Technologies
Redesigned piston bowl & injection
The piston bowl is modified for improved combustion. Peak cylinder pressure increased from 230 bar for the reference 2017 engine to 250 bar. Compression ratio also increased accordingly from 18.5 to 21, leading to further improved fuel economy. The injection system was updated to include 10 holes, improving the combustion uniformity.
Improved air handling
A ball bearing rotor was introduced in the in-house turbocharger which reduced friction, improved fuel efficiency by 0.4% and also reduced oil consumption. The turbine housing has two asymmetric volutes, one for EGR flow control and another for lambda control. This asymmetric configuration and a unique EGR valve allows for EGR rates up to 50% and 2 kW of turbo output. Furthermore, asymmetric fuel injection is used to run part of the cylinders on high EGR lean charge and the other on rich mixture. This leads to less efficient work transfer to the turbine and the enthalpy is transferred to the exhaust – making it hotter for improved NOx conversion.
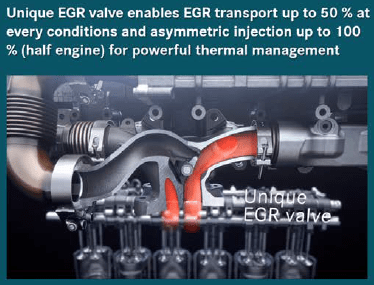
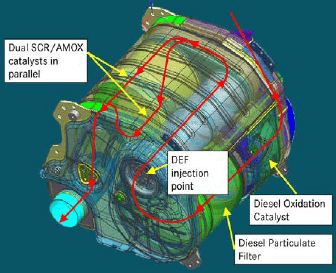
After-treatment system
The after-treatment system includes a diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC), a diesel particulate filter (DPF) and two SCR and ammonia slip catalysts each, in parallel. The diesel exhaust fluid dosing is optimized using control models. The design allows for high level of ammonia mixing and uniformity at the face of the SCR catalysts.
Compliance of low NOx emissions is ensured till end of useful life of 435,000 miles via testing on aged parts. It is noted that one of the key reasons for loss in NOx conversion is the variability in fuel quality, and engineering margins are set accordingly.
On the FTP cycle, NOx was reduced by 60% compared to the model year 2017 engine, while also reducing GHG emissions by 4%.
Other recent posts
Real-world CO2 emissions from cars and vans in Europe are 20% higher than certification values
EU Commission finds real-world CO2 emissions from cars and vans in Europe greatly exceed lab certification values. Plug-in hybrids are not being charged as much as estimated.
US EPA MY 2027-2032 Heavy-Duty Phase 3 GHG Standards
The U.S. EPA has finalized the Phase 3 GHG rule specifying CO2 emission reductions from heavy-duty trucks and buses over MY 2027 – 2032.
US EPA MY 2027-2032 Light-Duty CO2 Standards
The EPA final rule will require a fleet averaged 50% reduction in CO2 emissions for light-duty vehicles, over MY 2027 – 2032.
Like it ? Share it !
