Regulations
Summary of EV related U.S. Tariffs on Chinese Imports
As described by theWhite House and United States Trade Representative, May 14th, 2024
Background
In recent years, China has gained a significant lead when it comes to all decarbonization pathways – from manufacturing solar panels and electric vehicles to owning the mines and supply chain for making batteries. Europe has swung from an exporter to a net importer of vehicles from China, especially for electric vehicles. Several recent reports suggest that Chinese made EVs are not only cheaper but are also at par with their western counterparts for style and quality.
It is only a matter of time that they gain market share in the U.S. (if you are skeptical, remember that Japanese cars were never considered to be able to compete in the U.S. at one point ..)
The Biden Administration has established significant incentives to reshore production of EVs and related critical components. Now, it has published revised tariffs on several strategic products made in China. Here is a summary of the parts relevant to EVs and related materials.

Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Tariffs on EVs under Section 301 will rise from 25% to 100% in 2024.
- This tariff increase aims to protect American manufacturers from unfair trade practices and safeguard investments and jobs in the EV sector.
- The tariffs are aimed at ensuring a “made in America by American workers” future.
Batteries:
- China controls >80% of certain segments of the EV battery supply chain, seen as a risk to U.S. supply chains and national security.
- Tariffs on lithium-ion EV batteries will rise from 7.5% to 25% in 2024
- Natural graphite will face tariffs of 25%, as will permanent magnets, starting 2026. Other critical minerals will have the same tariffs, starting even earlier – this year.
Other Tariffs
While we focus here on transportation, this is a broader set of tariffs “across strategic sectors such as steel and aluminum, semiconductors, electric vehicles, batteries, critical minerals, solar cells, ship-to-shore cranes, and medical products”
This table provides a summary of all goods impacted.

Closing Remarks
Tariffs are meant to increase prices of and discourage imports, which in this case is seemingly at odds with the U.S. goal of accelerating decarbonization and addressing climate change. References to national security notwithstanding, ultimately these tariffs are about protecting jobs (especially in an election year).
Sign up here to receive such summaries and a monthly newsletter highlighting the latest developments in transport decarbonization
5-Min Monthly
Sign-up to receive newsletter via email
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Recent Posts
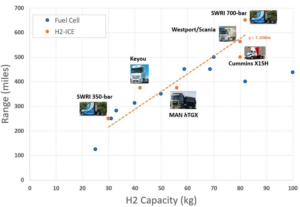
Conference Summary – Hydrogen for Sustainable Mobility Forum
![]()
A summary of the “Hydrogen for Sustainable Mobility Forum” conference held in Turin.
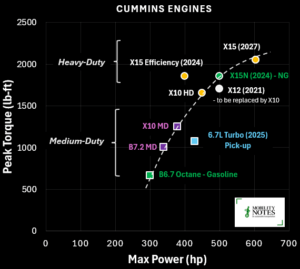
Cummins new engines introduced and poised to meet MY2027 standards
![]()
A round-up of the recently announced engines which will meet the upcoming EPA MY 2027 standards.
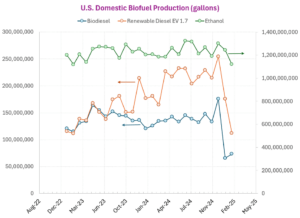
Biodiesel and Renewable diesel production in the US hits a speedbump
![]()
Biodiesel and renewable diesel production in the U.S. has slowed down significantly in 2025. Here’s why.

