Regulations
Summary of the near-final Euro 7 Regulation for passenger cars and heavy-duty vehicles
Minimal changes to LD limits, particles down to 10nm, limits for tires and battery state-of-health
We have covered the unfolding of Euro 7 emission standards for light- and heavy-duty vehicles in several past articles.
There seems to be light at the end of the Euro 7 tunnel: after several rounds of negotiations between the EU Commission, Council and Parliament, a near-final regulation has been published.
Here is a brief summary. If you need more details or have questions, please get in touch. Please understand that regulations are complex and need interpretation – this article will be updated based on further reading and any feedback.
Sign up here to receive such summaries and a monthly newsletter highlighting the latest developments in transport decarbonization
5-Min Monthly
Sign-up to receive newsletter via email
Thank you!
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
Recent Posts

Conference Summary – SAE WCX 2025
![]()
A summary of the “SAE WCX 2025” conference held in Detroit.
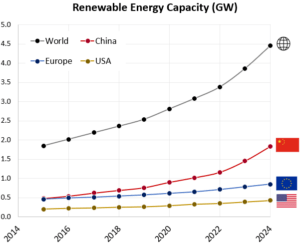
IRENA Renewable Energy Capacity Statistics 2025
![]()
According to the latest report from IRENA, 2024 saw the largest increase in renewable capacity, accounting for 92.5% of overall power additions.
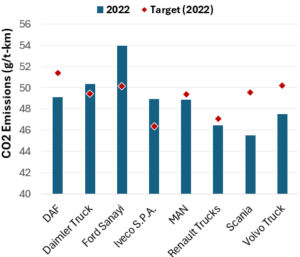
CO2 Emissions Performance of Heavy-Duty Vehicles in Europe – 2022 Results
![]()
The European Commission has published the official 2022 CO2 emission results for heavy-duty vehicles. Many OEMs are ahead of the targets and have gained credits, while others have their work cut out as we approach the 2025 target.

